|
Phongo Clap RT
1.0
Simple Raytracing Renderer
|
|
Phongo Clap RT
1.0
Simple Raytracing Renderer
|
Core of my program, central unit that manages all the other classes almost. More...
#include <Renderer.h>
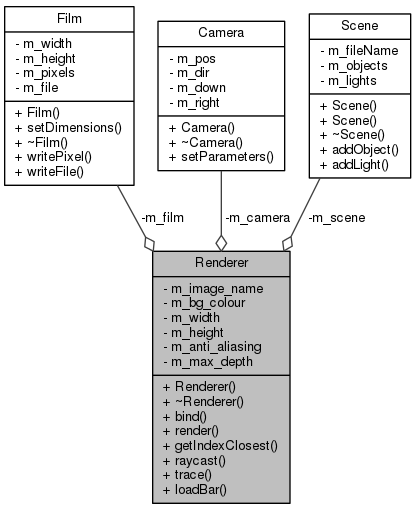
Public Member Functions | |
| Renderer () | |
| Constructor for the renderer class. More... | |
| ~Renderer () | |
| Destructor, frees any possible memory from the heap. More... | |
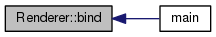
| void | bind (Scene *_scence, Film *_film, Camera *_camera, int _max_depth, int _anti_aliasing, std::string _image_name) |
| Grabs all the information and places it into the private interface. More... | |
| void | render () |
| Will trigger the class and start doing all the calculations. More... | |
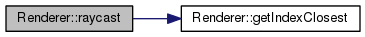
| int | getIndexClosest (std::vector< double > _intersections) |
| Given an intersections vector will return the closest to the camera, the one that it will read colour from. More... | |
| bool | raycast (ngl::Vec3 _from, int _avoid) |
| Will fire rays from a position, then iterate over the lights, and if any object is inbetweet will return true as value, that means that this particular point has to be shadowed. More... | |
| ngl::Colour | trace (ngl::Vec3 _from, ngl::Vec3 _direction, int _depth) |
| Probably the most important algorithm of this class. This method is recursive. It will fire a ray from the given position in the first parameter aiming towards the direction specified in the second one. If it hits a reflective or refractive material the new reflection/transimission ray will be calculated and this method will be called again. The limiter will be the depth argument. More... | |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static void | loadBar (int x, int n, int r, int w) |
| Implements a loading bar. This algorithm is taken from another person. More... | |
Private Attributes | |
| std::string | m_image_name |
| Name of the filename that will be written. More... | |
| Film * | m_film |
| Associated film. More... | |
| Scene * | m_scene |
| Associated scene. More... | |
| Camera * | m_camera |
| Associated camera. More... | |
| ngl::Vec3 | m_bg_colour |
| default background colour. More... | |
| int | m_width |
| Width of the image. More... | |
| int | m_height |
| Height of the image. More... | |
| int | m_anti_aliasing |
| Antialiasing amount. More... | |
| int | m_max_depth |
| Maximum number of ray stack frames. More... | |
Core of my program, central unit that manages all the other classes almost.
Definition at line 23 of file Renderer.h.
| Renderer::Renderer | ( | ) |
| Renderer::~Renderer | ( | ) |
Destructor, frees any possible memory from the heap.
Definition at line 47 of file Renderer.cpp.
References Scene::m_lights, Scene::m_objects, and m_scene.
| void Renderer::bind | ( | Scene * | _scence, |
| Film * | _film, | ||
| Camera * | _camera, | ||
| int | _max_depth, | ||
| int | _anti_aliasing, | ||
| std::string | _image_name | ||
| ) |
Grabs all the information and places it into the private interface.
| [in] | _scene | Scene which will contain all the lights, objects, etc... |
| [in] | _film | Film structure to query the width, height and other attributes from. |
| [in] | _camera | Camera used to fire the primary and secondary rays. |
| [in] | _max_depth | Maximum depth of recursion. |
| [in] | _anti_aliasing | Amount of antialiasing. |
| [in] | _image_name | The image filename. |
Definition at line 59 of file Renderer.cpp.
References m_anti_aliasing, m_bg_colour, m_camera, m_film, Film::m_height, m_height, m_image_name, m_max_depth, m_scene, Film::m_width, and m_width.
| int Renderer::getIndexClosest | ( | std::vector< double > | _intersections | ) |
Given an intersections vector will return the closest to the camera, the one that it will read colour from.
| [in] | _intersections | Vector with all the 't' parameters from the ray equation 1R = O + t * d` (intersection) |
Definition at line 72 of file Renderer.cpp.

|
inlinestatic |
Implements a loading bar. This algorithm is taken from another person.
| [in] | x | Current value (in my case the current pixel expressed as y * height + x. |
| [in] | n | Total number of elements (in my case width/height). |
| [in] | r | Number of times for the bar to be refreshed. |
| [in] | w | Width in characters of the loading bar. |
The following section is from :- Hemsley, R.(2011). Creating a progress bar in C/C++ (or any other console app). [online] [Accessed 2015]. Available from: https://www.ross.click/2011/02/creating-a-progress-bar-in-c-or-any-other-console-app/.
Definition at line 21 of file Renderer.cpp.

| bool Renderer::raycast | ( | ngl::Vec3 | _from, |
| int | _avoid | ||
| ) |
Will fire rays from a position, then iterate over the lights, and if any object is inbetweet will return true as value, that means that this particular point has to be shadowed.
| [in] | _from | (in world space) where to fire the ray from |
| [in] | _avoid | Will make sure that there is no self-shadowing, the shadowing effect is thus sold by the shading model. This is the index of the object which has to be ignored when finding the shadowing objects. |
Definition at line 107 of file Renderer.cpp.
References getIndexClosest(), Scene::m_lights, Scene::m_objects, and m_scene.

| void Renderer::render | ( | ) |
Will trigger the class and start doing all the calculations.
Definition at line 322 of file Renderer.cpp.
References loadBar(), m_anti_aliasing, m_camera, Camera::m_dir, Camera::m_down, m_film, Film::m_height, m_image_name, Camera::m_pos, Camera::m_right, Film::m_width, trace(), Film::writeFile(), and Film::writePixel().
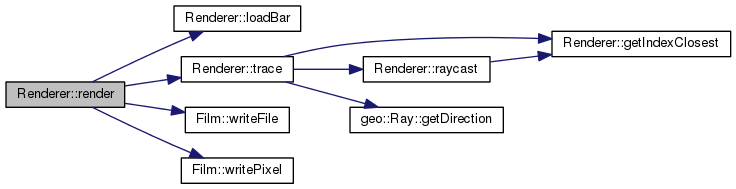
| ngl::Colour Renderer::trace | ( | ngl::Vec3 | _from, |
| ngl::Vec3 | _direction, | ||
| int | _depth | ||
| ) |
Probably the most important algorithm of this class. This method is recursive. It will fire a ray from the given position in the first parameter aiming towards the direction specified in the second one. If it hits a reflective or refractive material the new reflection/transimission ray will be calculated and this method will be called again. The limiter will be the depth argument.
| [in] | _from | Position where to fire the ray from. |
| [in] | _direction | Aim vector that defines the directions in which we want to fire the ray. |
| [in] | _avoid | Index of the object we want to avoid. By index I mean the position in the m_scene_objects vector. |
Definition at line 142 of file Renderer.cpp.
References geo::Ray::getDirection(), getIndexClosest(), Scene::m_lights, m_max_depth, Scene::m_objects, m_scene, and raycast().

|
private |
Antialiasing amount.
Definition at line 117 of file Renderer.h.
|
private |
default background colour.
Definition at line 105 of file Renderer.h.
|
private |
Associated camera.
Definition at line 101 of file Renderer.h.
|
private |
Associated film.
Definition at line 93 of file Renderer.h.
|
private |
Height of the image.
Definition at line 113 of file Renderer.h.
|
private |
Name of the filename that will be written.
Definition at line 89 of file Renderer.h.
|
private |
Maximum number of ray stack frames.
Definition at line 121 of file Renderer.h.
|
private |
Associated scene.
Definition at line 97 of file Renderer.h.
|
private |
Width of the image.
Definition at line 109 of file Renderer.h.
 1.8.9.1
1.8.9.1